Symptoms, treatment… everything you need to know about Mycoplasma pneumoniae, the bacteria that causes tonsillitis, bronchitis, pneumonia
Les enfants et les jeunes adultes sont en première ligne. SEVEMENT/PIXABAY
The number of infections caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae has continued to rise since it was spotted at the end of summer: according to Public Health France, the bacteria is responsible for 30% 50% of pneumonia in children. Adults aged 40 are also on the front line. Valérie Ertel-Pau, deputy head of the Good Practices Department at the High Authority for Health, explains the challenges of appropriate care.
Valérie Ertel-Pau is head of the good practices department at the High Authority for Health (HAS).

Valérie Ertel-Pau: "Wear a mask in case of respiratory symptoms". DR HAS
The bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae is "the'surprise guest" of this winter ?
Mycoplasma pneumoniae causes cyclical epidemics every three to seven years. This is not a new bacteria, it is a known bacteria, it is the second cause of acute community pneumonia, that is to say pneumonia contracted outside of a hospital setting. We know the clinical picture and the treatments very well, this is not a surprise.
Its emergence is undoubtedly linked to the lifting of barrier gestures, and in particular the absence of wearing a mask. This is one of the essential messages: you must put the mask back on in the event of respiratory symptoms.
Faced with this situation, the High Authority for Health was contacted by the Ministry of Health to remind professionals of the essential elements, the symptoms and the actions to take to make a diagnosis and treatment .
The last epidemic linked to Mycoplasma pneumoniae dates back to before Covid ?
This bacteria is there all the time! When we talk about acute community-acquired bacterial pneumonia, the most common origin is pneumococcus, which gives a different clinical picture, with another treatment.
What are the symptoms of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection ?
Nothing is specific to this bacteria. Respiratory infection manifests itself with cough, low-grade fever, headache, muscle and joint pain, sometimes discomfort and shortness of breath. But you should know that the majority of infections linked to this bacteria are benign, we do not necessarily need antibiotics when we have manifestations such as bronchitis.
We only put people who have pneumonia, including a persistent cough and fever, on antibiotics. The others will not receive treatment.
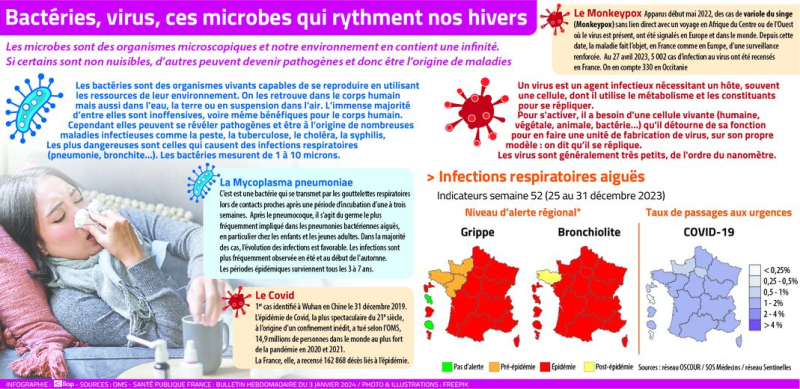
These viruses and bacteria that make us sick.
How is pneumonia linked to Mycoplasma pneumoniae treated ?
With antibiotics from the macrolide class, also used for tonsillitis, in particular: azythromycin or clarythromycin. For pneumococcal pneumonia, the treatment is amoxicillin. If amoxicillin is prescribed against Mycoplasma pneumoniae, it will be ineffective and the patient's condition will not improve. It will be necessary to "switch" antibiotics.
"The symptoms will set in gradually while pneumococcal pneumonia will have a sudden onset"
What could suggest an infection caused by this bacteria ?
A gradual onset of symptoms, whereas pneumococcal pneumonia will have a sudden onset. With a good questioning of the doctor and a pulmonary auscultation which is not specific, the doctor can direct his diagnosis towards this pathology and request an X-ray of the lungs to confirm his diagnosis and look for complications. For patients with chronic illnesses, the attending physician will be on alert.
There is no simpler test, respiratory or blood ?
In community medicine, no. But for more serious clinical conditions which land a patient in hospital, there may be access to PCR tests which are not carried out on an outpatient basis.
But it's often complicated to get a quick imaging exam…
Yes, that's why in case of suspicion, we recommend implementing treatment immediately. Radiography should not delay taking antibiotics. If the diagnosis is correct, the patient on macrolides will get better quickly, in 48 hours to 72 hours. Otherwise, you will need to contact your doctor again, as you may be facing complications. But it's rare.
The bacteria was spotted at the end of summer, how long does an epidemic last ?
It's variable, there are also other respiratory illnesses of winter: the flu, Covid, or those induced by RSV, without forgetting that' ;there may be co-infections.
I subscribe to read more




